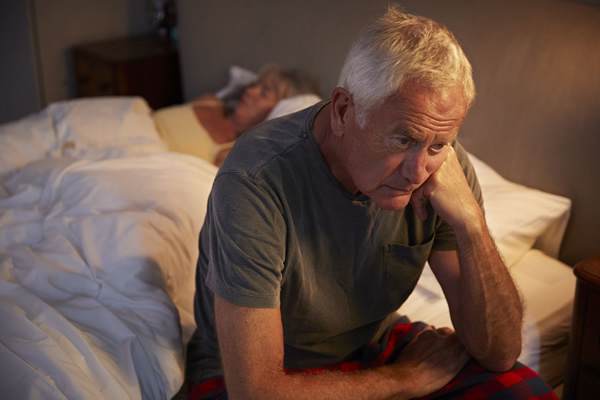
The relationship between poor sleep and mental health issues is a topic of growing interest and concern in contemporary research and public health discourse. While the importance of sleep for overall well-being has long been recognized, recent studies have shed light on the profound impact that inadequate or disrupted sleep can have on mental health.
This introduction will explore the intricate link between poor sleep and mental health issues, delving into the bidirectional relationship between the two domains and highlighting the implications for individual health and societal well-being. From insomnia to sleep disorders like sleep apnea, understanding how sleep disturbances contribute to conditions such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment is crucial for developing effective interventions and promoting optimal mental health outcomes.
Understanding the Connection Between Sleep and Mental Health
Understanding the intricate connection between sleep and mental health is paramount in comprehending the holistic well-being of individuals. Sleep serves as a fundamental pillar of mental health, intricately intertwined in a bidirectional relationship. While mental health issues can disrupt sleep patterns, poor sleep quality or deprivation can exacerbate existing mental health conditions or even trigger new ones. Research has shown that adequate, high-quality sleep is crucial for cognitive functions, emotional regulation, and overall psychological resilience. Recognizing and addressing the connection between sleep and mental health is essential for promoting comprehensive wellness strategies and enhancing mental health outcomes.
The Science of Sleep

The Science of Sleep delves into the intricate mechanisms governing our restorative nightly repose and its profound impact on our well-being. It encompasses the study of sleep stages, cycles, and the physiological processes underlying them. Understanding the connection between sleep and mental health is central to this discipline, as research continually reveals how insufficient or disrupted sleep can significantly affect our cognitive functions, emotional regulation, and overall mental wellness. This connection underscores the vital importance of prioritizing quality sleep for optimal psychological health and resilience.
The Consequences of Sleep Deprivation

The consequences of sleep deprivation are multifaceted and impactful, encompassing various aspects of physical and mental well-being. Notably, the connection between sleep and mental health is profound, with sleep deprivation exacerbating conditions such as depression, anxiety, and stress. When sleep is insufficient, cognitive functions like memory, attention, and decision-making suffer, impairing daily functioning and productivity.
Moreover, chronic sleep deprivation heightens the risk of developing serious health issues such as cardiovascular diseases, obesity, and diabetes. Addressing the intricate connection between sleep and mental health is crucial for fostering overall well-being and promoting resilience against the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation.
The Neurochemical Connection
The intricate relationship between various neurotransmitters and hormones within the brain, influences cognitive functions, emotions, and behavior. This intricate network governs everything from mood regulation to learning and memory. One particularly significant aspect of this connection is its role in the connection between sleep and mental health. Research suggests that neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA play crucial roles in both regulating sleep patterns and managing mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Imbalances in these neurochemicals can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to mental health issues, while addressing sleep problems can often improve mental well-being. Understanding this link offers valuable insights into therapeutic approaches for mental health conditions, highlighting the importance of addressing sleep quality for overall psychological wellness.
Sleep Disorders and Their Mental Health Implications
Sleep disorders refer to a range of conditions that disrupt normal sleeping patterns, encompassing issues like insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy. These disorders not only interfere with the quantity and quality of sleep but also have significant implications for mental health. Research consistently highlights the intricate connection between sleep and mental health, suggesting that disruptions in sleep can exacerbate or even precipitate various mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder.
Conversely, untreated mental health issues can contribute to the development or exacerbation of sleep disorders. Understanding and addressing this link is crucial for effective treatment and management of both sleep disorders and mental health conditions.
Sleep Hygiene and Mental Well-being
Sleep hygiene refers to a set of practices and habits that promote quality sleep and overall well-being. It encompasses behaviors such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, limiting caffeine and electronics before bedtime, and engaging in relaxation techniques.
Mental well-being, on the other hand, refers to a state of emotional and psychological balance where individuals can cope with stress, realize their potential, and contribute meaningfully to their communities. The connection between sleep and mental health is profound; poor sleep hygiene can exacerbate mental health issues such as anxiety and depression while prioritizing good sleep habits can significantly improve mood, cognitive function, and overall mental well-being. Therefore, fostering healthy sleep habits is essential for maintaining optimal mental health.
The Role of Psychological Interventions
The role of psychological interventions encompasses a range of therapeutic techniques aimed at addressing various mental health concerns. These interventions are pivotal in fostering emotional well-being, enhancing coping mechanisms, and promoting overall psychological resilience. Particularly significant is their role in elucidating and addressing the intricate connection between sleep and mental health.
Research has consistently demonstrated the profound impact of sleep on mental well-being, with disturbances in sleep patterns often exacerbating symptoms of psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. Psychological interventions play a crucial role in this context by offering tailored strategies to improve sleep quality, regulate sleep-wake cycles, and alleviate associated psychological distress. By addressing the intricate interplay between sleep and mental health, these interventions contribute significantly to holistic approaches to mental health care.
Medications and Their Impact
Medications refer to pharmaceutical substances prescribed to treat various medical conditions. Their impact spans a broad spectrum, influencing bodily functions, alleviating symptoms, and promoting health. When considering the connection between sleep and mental health, medications play a crucial role. Certain medications, such as antidepressants or antipsychotics, can affect sleep patterns directly, either by promoting or disrupting sleep.
Additionally, addressing sleep disturbances through medication can have a significant impact on mental health outcomes, as inadequate sleep is closely linked to conditions like depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. Thus, medications serve as a vital tool in managing the intricate link between sleep and mental well-being, offering avenues for treatment and symptom relief.
Mental Health Interventions for Better Sleep
Mental health interventions for better sleep aim to address the intricate connection between sleep and mental health, recognizing that disrupted sleep patterns can exacerbate mental health challenges and vice versa. These interventions encompass a range of strategies tailored to individual needs, including cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), mindfulness practices, relaxation techniques, and lifestyle adjustments.
By targeting both the physiological and psychological aspects of sleep disturbances, these interventions foster improved sleep quality and duration, which in turn can alleviate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. Emphasizing the bidirectional relationship between sleep and mental well-being, such interventions provide holistic support to promote overall health and resilience.
The Role of Lifestyle Factors
The role of lifestyle factors encompasses various aspects of daily living that significantly impact overall well-being. These factors, ranging from diet and exercise to stress management and social connections, play a crucial role in maintaining physical and mental health. One particularly noteworthy connection lies in the connection between sleep and mental health. Adequate sleep is fundamental for cognitive function, emotional regulation, and overall mental wellness.
Disrupted sleep patterns, such as insomnia or irregular sleep schedules, have been strongly associated with an increased risk of developing various mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. Conversely, prioritizing good sleep hygiene can serve as a protective factor, promoting resilience against mental health challenges. Thus, understanding and addressing the intricate relationship between sleep and mental health is essential for fostering holistic well-being.
Cultural and Societal Factors
Cultural factors refer to the norms, beliefs, values, and practices shared by a particular group of people, influencing their behaviors and perceptions. Societal factors encompass the broader structures and systems within a society, such as institutions, policies, and economic conditions, which shape individuals’ lives and interactions.
When considering the connection between sleep and mental health, cultural factors might include cultural attitudes towards sleep, such as norms around bedtime routines or perceptions of sleep as a priority. Societal factors could involve access to healthcare services for sleep disorders or employment practices affecting sleep patterns. Understanding these cultural and societal influences is crucial in comprehending how they impact the connection between sleep and mental health, as they shape individuals’ behaviors and access to resources that can affect both sleep quality and mental well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the connection between sleep and mental health is paramount for comprehending the holistic well-being of individuals. Cultural factors, encompassing norms and beliefs surrounding sleep, and societal factors, such as access to healthcare services, play pivotal roles in shaping this relationship. The bidirectional influence between sleep and mental health highlights the importance of addressing both domains for optimal psychological wellness. Recognizing and addressing these cultural and societal influences are essential steps in promoting comprehensive wellness strategies and enhancing mental health outcomes.